
Tangible Landscape
A TANGIBLE INTERFACE FOR GEOSPATIAL MODELING
Tangible Landscape
Hand-on Terrain Learning Kit
Over the past two decades, Tangible Interaction has grown as a field of study to be the subject of prolific and visionary research across the globe. The focus of this research has been widely varied, from assisted living to art installations. Tangibles for learning, however, have been a consistent theme over the years, as the potential of tangible systems for this purpose has become more and more apparent. Tangible Interaction as a framework for developing pedagogical systems and products has the ability to excite and engage students with topics in ways not achievable using traditional teaching tools. In the following, the underlying concepts of this area are discussed, along with the potential benefits they present for learning.
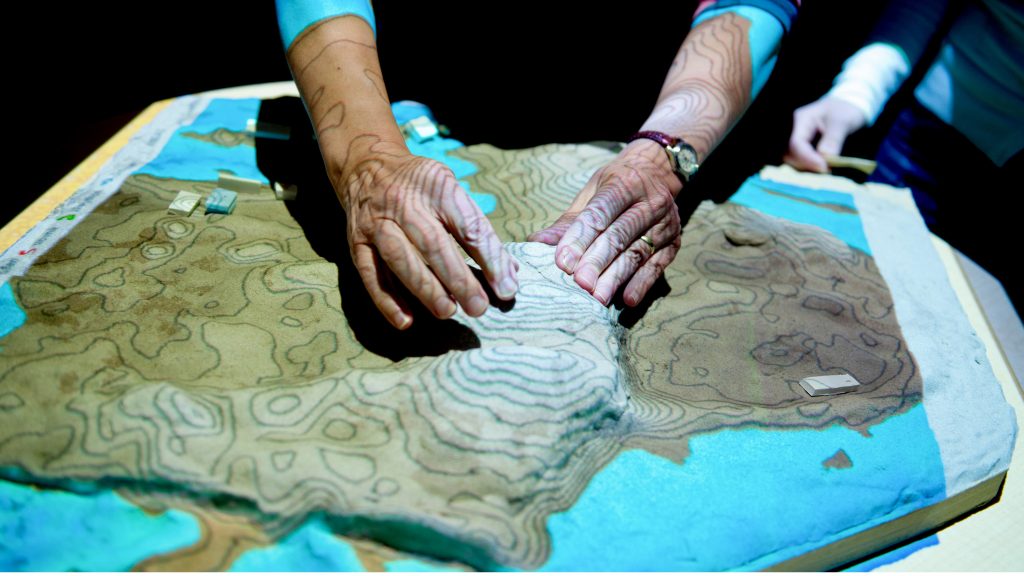
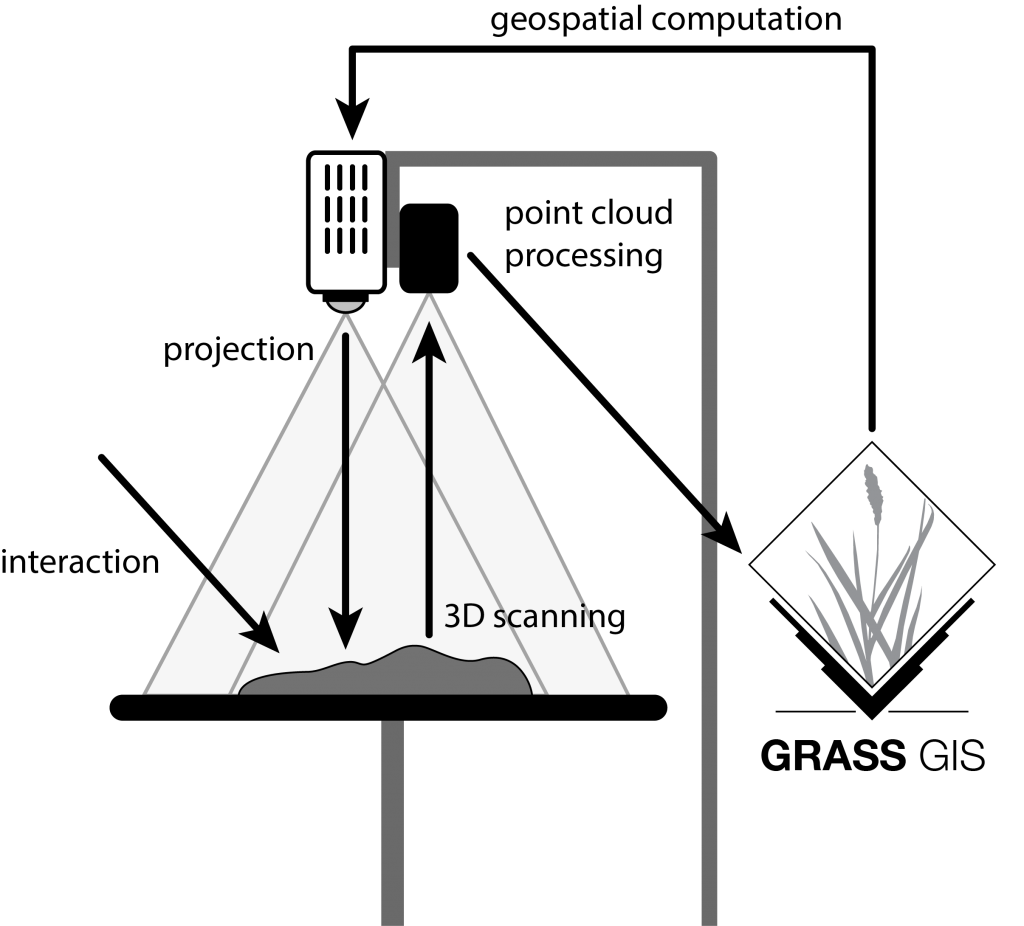

Tangible Landscape
“The system allows participants with different backgrounds to collaborate on finding effective solutions to land-management problems.”
Helena Mitasova,
Professor Associate Director for Geovisualization at the Center for Geospatial Analytics
What is Tangible?
Put simply, Tangible Interaction refers to the concept of interacting with the digital world using physical objects, gestures and behaviours in familiar or intuitive ways. People can access and manipulate digital data instinctively using recognisable objects and motions. For example, a student could receive reminders about what books to bring to class or if they are running late from their digitally-augmented schoolbag through audio, visual or haptic outputs. Another example is Reactable, a Tangible Interaction interface designed to support multi-user creation and interaction with music through the movement of plastic cubes on a digitally- mediated table. In a world dominated by screen-based technologies, the field of Tangible Interaction has come to be regarded as an effective way to engage people and provide them with a novel yet instinctive method of engaging with the digital world.
How can it benefit learning?
Tangible Interaction allows students to go beyond the screen and actually physically interact with objects that reveal information on the subjects they are learning. A number of concepts behind Tangible Interaction support this, including the idea of multi-sensory interfaces and support for experimentation.
Basic Landscape Features
- Processing and analyzing the scanned DEM
- Topographic analysis of graded landscape
Advance Landscape Features
- - Surface water flow analysis
- Viewshed analysis
- Trail planning
-Solar radiation dynamics
Contact Tangible Team
i-bitz company limited
Head Quarter
1371 Suite 10 Capital Mansion, Phahonyothin Rd, Phayathai, Bangkok, 10400 Thailand

